LDPE and HDPE: Key Differences & Similarities
What Is PE (Polyethylene)?
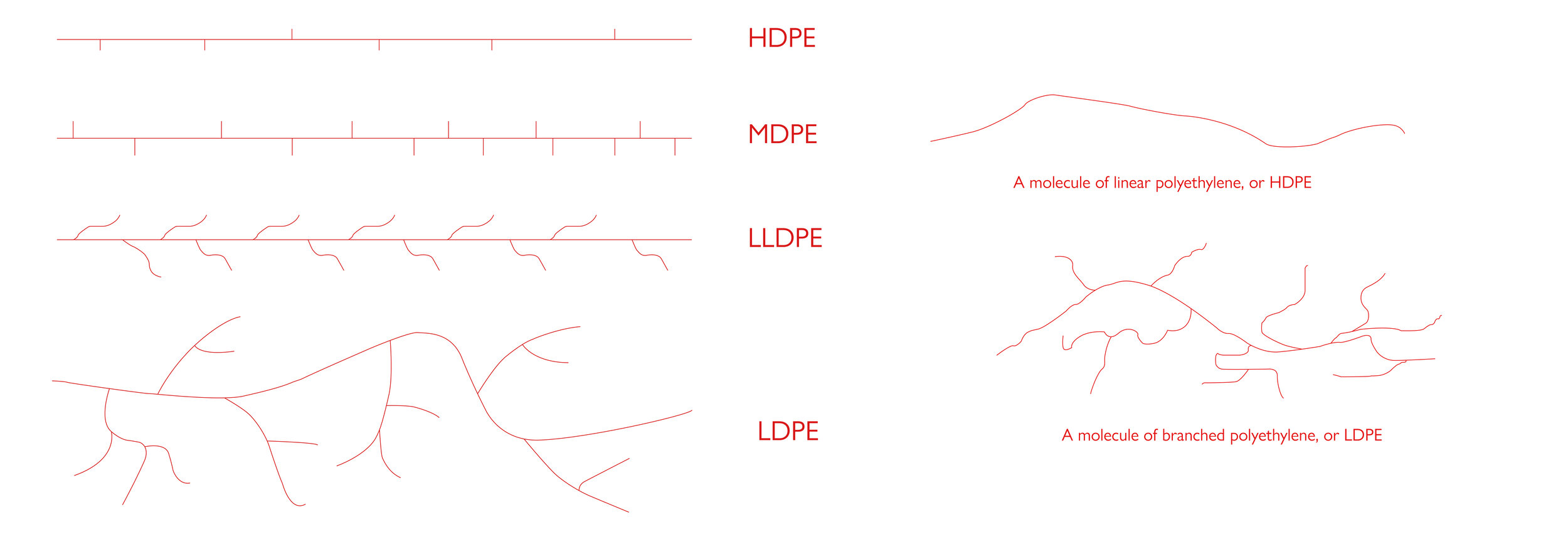
Before diving into the differences between LDPE and HDPE, let us understand what ‘PE’ is. PE or Polyethylene is the most common form of plastic used in consumer products. Globally we produce and use about 80 million tons of PE every year! PE is a thermo-plastic that is created through a process of polymerising ethylene, hence the name polyethyelene. This process produces very long and straight chains of hydrocarbon monomers. It is through this process that we can adjust the length of these branches to make difference types of PE, just like LDPE and HDPE.
Low-Density & High-Density
So what exactly is LDPE and HDPE? As we mentioned earlier, during the polymerisation process we can change the length of the hydrocarbon monomer branches. Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) has the most long- and short-chain branching resulting in its lower density. The long branches keep the molecular chains from packing tightly thus resulting in a lower density. It is due to this lower density that LDPE has less tensile strength but allows for greater ductitlity (ability to be deformed). Due to its ductility, LDPE is useful for a wide range of applications from rigid products such as plastic bottles to flimsy ones such as grocery bags and stretch wrap.
As you have probably guessed by now, HDPE stands for High-Density Polyethylene. HDPE has minimal branching of hydrocarbon monomer branches which allows the molecules to pack together more densely, hence the name. This gives HDPE a more rigid characteristic and added tensile strength. This added strength makes it ideal for applications that require a bit more rigidity such as milk and detergent jugs.
An illustration of how polyethyelene branches differ in length between the varying densities, primarily LDPE and HDPE.
Key Differences
Due to the differences in density, LDPE and HDPE possess different properties beyond their ductility and tensile strength. Below is a table that summaries some key differences that might determine which material is more suitable for certain applications. For example, due to the lower density of LDPE, bags and sheets made using LDPE can be made to be more transparent than HDPE which possesses a more milky, translucent colour by nature. This would make LDPE bags more suitable if showcasing a product is crucial or being able to identify the contents of the packaging is important. In other cases, heat resistance might be more important which would make HDPE the more obvious choice.
| Property | LDPE | HDPE |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | More flexible due to low density | More rigid due to high density |
| Heat Resistance | Low heat resistance | Can withstand more than 100C |
| Clarity | High clarity | Low clarity |
| Melting Point | ~115C | ~135C |
LDPE (left) provides for greater clarity than HDPE (right). Sometimes your choice of which material will come down to the clarity you require.
Choosing The Right Material
Now, you might be asking: which is the right material for my use case? The answer to that question would depend on the application or intended use for the bag or sheet. Although, sometimes it is up to personal preference as well! For example, our pallet covers can be made with LDPE or HDPE, both of which serve the same purpose and do a great job at protecting pallets from dust and rain. It just depends if you would like a clear cover or a slightly translucent cover. That might not really answer your question and leave you worried, but do not worry!
If you are unsure of which material you need for your packaging needs, you can rely on our extensive experience to know which is best for you. All you have to do is explain to us your use case and any specific requirements you may have that will help us determine the best solution for you.
If you have any questions about our services, click here.
Or to see what products we manufacture, click here.